
INTRODUCTION
This article emphasizes the significance of technology for the education system in Nigeria, highlighting its potential to advance compliance with global trends. It also presents valuable insights into the impact of technology on the education sector in different countries, especially in developed nations such as Canada and the United States. Furthermore, the article suggests solutions to the challenges impeding the full implementation of technological advancements in the sector, thereby promoting strategic growth for the Nigerian education system to match up to its global counterparts.
The emergence of the internet has revolutionized the world, creating a unified global community where individuals can connect with others from various locations, all from the comfort of their own spaces. Technological innovation and creativity have played a crucial role in driving human progress and have become essential tools for fostering excellence in any field.
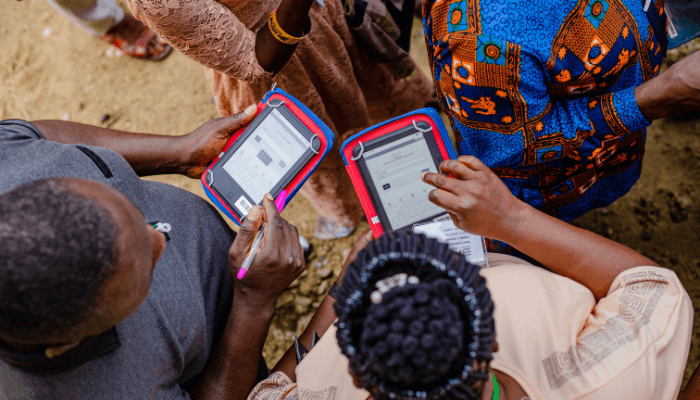

According to Fela (2021), technology has had a significant impact on education by enhancing the overall learning experience through the use of various tools such as cloud computing, speech-to-text options, artificial intelligence, and learning analytics. Gregy (2024) further emphasizes the ongoing role of technology in education, highlighting its potential to restructure the system and improve the teaching-learning process. This underscores the importance of integrating technology into the education sector to enhance educational outcomes and promote effective learning. Kehinde (2022) also refers to ‘edutech’ as the integration of computer hardware and software to enhance the learning process.
However, the implementation of this concept in Nigeria is quite low, and its ability to improve the quality of education in the country is not yet evident. Statistics from the Nigerian Bureau of Statistics reveal that only about 22% of schools in the country have access to computers and the internet. This percentage is incredibly low and is largely attributed to financial constraints within the sector, compounded by the government’s unwillingness to invest in public institutions and enhance their competitiveness with counterparts abroad.
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the negative impact of lockdown measures, leading to school closures and emphasizing the importance of technology in education. In response to this, many schools transitioned to online classes. However, this shift presented challenges for students unfamiliar with digital platforms, who were accustomed to traditional learning methods. Submitting assignments via email instead of on paper and using tools like Canva and Microsoft PowerPoint for presentations were new concepts for many of them. The traditional practice of writing notes on chalkboards was also disrupted.
According to a report generated by the International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA), titled “Computers in Education: Comparing Use Across Countries,” approximately 90% of students in grades 6 to 12 have access to computers at school, with approximately 85% having access to the internet while at school. Additionally, in terms of technology adoption at home, roughly 80% of students in grades 6 to 12 have access to computers at home, with about 70% having access to the internet at home. Notably, in the United States, approximately 95% of students in grades 6 to 12 have access to computers at school, while approximately 90% have access to the internet at home. These impressive percentages are a testament to the commitment of governments and stakeholders to the adoption of technology for the benefit of students’ academic performance.
It is highly recommended that comprehensive training sessions be provided for teachers and lecturers in primary, secondary, and tertiary institutions on effectively utilizing technological innovations and tools to enhance the teaching-learning process. Private institutions should also be required to ensure compliance. Substantial funds should be invested heavily in acquiring these tools for public schools nationwide. While the adoption of technology for the annual Unified Tertiary Matriculation Examination (UTME) organized by the Joint Admission and Matriculation Board (JAMB) is commendable, it is important to note that the nation has not fully utilized its potential to revolutionize the education sector.
________________
REFERENCES
Greg T. (2024). ”Technology Unlocks Educational Boundaries.” Educate.NG
Fela, B. (2021). “Bridging the Technology Gap in the Nigerian Education System.” The Cable.
Kehinde O. (2022). “The Need for Nigeria’s Education System to Adopt Technology.” Vanguard.
Samuel Tolulope Alimi is the founder and lead scholar at English TV, an online platform dedicated to teaching the English language on various social media platforms. He earned a BA (Ed) from the prestigious Olabisi Onabanjo University, Ogun State, where he majored in English and Education.
As a Grammar Columnist at Peoples Daily newspaper, one of the foremost and trusted national newspapers, he writes about Nigerian English on Page 23 of every Saturday’s publication, with his column titled “Common Errors in English with Samuel Alimi.” His writings have attracted considerable readership across several states, with over 30 detailed articles published.

















































































 EduTimes Africa, a product of Education Times Africa, is a magazine publication that aims to lend its support to close the yawning gap in Africa's educational development.
EduTimes Africa, a product of Education Times Africa, is a magazine publication that aims to lend its support to close the yawning gap in Africa's educational development.